Arago, technology platform in optics for the industrial sector
 Arago is a technology platform specializing in applied optics, based at IMT Atlantique’s Brest campus. It provides scientific services and a technical environment for manufacturers in the optics and vision sectors. It has unique expertise in the field of liquid crystals, micro-optics and health.
Arago is a technology platform specializing in applied optics, based at IMT Atlantique’s Brest campus. It provides scientific services and a technical environment for manufacturers in the optics and vision sectors. It has unique expertise in the field of liquid crystals, micro-optics and health.
Are you in the industrial sector or a small business wanting to experiment with a disruptive innovation? Perhaps you are looking for innovative technological solutions, but don’t have the time, or the technical means, to do so? The solution might be to try your luck with a technology platform.
Arago can help you to turn your new ideas into a reality. Arago was designed to foster innovation and technology transfer in research. It is home to highly-skilled scientists and technological facilities. Nexter, Surys and Valéo are among the companies who have already placed their trust in the platform, a component of Carnot Télécom and Société Numérique, specialized in the field of optics. Arago has provided them with access to a variety of high-end technology solutions for design, modeling, creating micro-optics, electro-optic functions based on liquid crystals, and composite materials for vision and protection. The fields of application are varied, ranging from protective and corrective glasses to holographic marking. It all involves a great deal of technical expertise, which we discussed step by step with Jean-Louis de Bougrenet, researcher at IMT Atlantique and the creator of the Arago platform.
Health and impact measurement of new technologies
Health is a field which benefits directly from Arago’s potential. The platform can directly count on the Health Interest Group 3D Fovéa, which includes IMT Atlantique, the University Hospital of Brest, and INSERM, and which led to the creation of the spinoff Orthoptica (the French leader in digital orthoptic tools). Thanks to Orthoptica, the platform was able to set up Binoculus, an orthoptic platform.
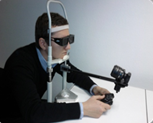 This operates as a digital platform and aims to replace the existing tools used by orthoptists, which are not very ergonomic. This technology consists solely of a computer, a pair of 3D glasses, and a video projector. It makes the technology more widely available by reducing the duration of tests. The glasses are made with shutter lenses, allowing the doctor to block each eye in synchronization with the material being projected. This othoptic tool is used to evaluate the different degrees of binocular vision. It aims to help adolescents who have difficulties with fixation or concentration.
This operates as a digital platform and aims to replace the existing tools used by orthoptists, which are not very ergonomic. This technology consists solely of a computer, a pair of 3D glasses, and a video projector. It makes the technology more widely available by reducing the duration of tests. The glasses are made with shutter lenses, allowing the doctor to block each eye in synchronization with the material being projected. This othoptic tool is used to evaluate the different degrees of binocular vision. It aims to help adolescents who have difficulties with fixation or concentration.
Acting for health now is worthwhile, but anticipating the needs of the future is even better. In this respect, the platform plays an important role for ANSES[1] in the evaluation of risks involved in deploying new immersive technology such as the Oculus Vive augmented reality headsets. “When the visual system is involved, an impact study with scientific and clinical criteria is essential”, explains Jean-Louis de Bougrenet. These evaluations are based on in-depth testing carried out on clinical samples, in liaison with hospitals such as Necker, HEGP (Georges Pompidou) and the University Hospital of Brest.
Applications in diffractive micro-optics and liquid crystal
At the same time, Arago has the expertise of researchers with several decades of experience in liquid crystal engineering (Pierre-Gilles de Gennes laboratory). “These materials present significant electro-optical effects, enabling us to modulate the light in different ways, at very low voltage”, explains Jean-Louis de Bougrenet.
 The researchers have used liquid crystals for many industrial purposes (protection goggles, spectral filters, etc.). In fact, liquid crystals will soon be part of our immediate surroundings without us even knowing. They are used in flat screens, 3D and augmented reality goggles, or as a camouflage technique (Smart Skin). To create these possibilities, Arago’s manufacturing and testing facilities are unique in France (including over 150m² of cleanrooms).
The researchers have used liquid crystals for many industrial purposes (protection goggles, spectral filters, etc.). In fact, liquid crystals will soon be part of our immediate surroundings without us even knowing. They are used in flat screens, 3D and augmented reality goggles, or as a camouflage technique (Smart Skin). To create these possibilities, Arago’s manufacturing and testing facilities are unique in France (including over 150m² of cleanrooms).
Other objects are also omnipresent in our daily lives, and even involve our smartphones: diffractive micro-optics. One of their specific features is that they exist in different sizes. Arago has all the tools necessary to design and produce these optics at different scales both individually and collectively, with easily-industrialized nano-imprint duplication processes. “We use micro-optics in many fields, for example manufacturing security holograms, biometric recognition, quality control and the automobile sector”, explains Jean-Louis de Bougrenet. Researchers recently set up a so-called two-photon photopolymerization technique, which allows the direct fabrication of fully 3D nanostrutures.
European ambitions
Arago is also involved in many other projects. Since 2016, it has hosted an IRT BCom platform. This platform is dedicated to creating very high-speed optical transmission systems in free space, for wireless connections for virtual reality headsets in environments such as the Cave Automatic Virtual Environment (CAVE).
Arago is already firmly established in Brittany, having recently finalized a technology partnership with the INL (International Iberian Nanotechnology Laboratory, a European platform similar to CERN). The partnership involves pooling resources, privileged access to technology, and the creation of joint European projects. The INL is unique in the European field of nanoscience and nanotechnology. Arago contributes the complementary material components it had been lacking. For Jean-Louis de Bougrenet, “in the near future, Arago will become part of the European technology cluster addressing new industrial actors, by adding to our offering and more easily integrating European programs with a sufficient critical mass. This partnership will enable us to develop our emerging activity in the field of intelligent sensors for the environment and biology”.
[1] ANSES: French Agency for Food, Environmental and Occupational Health & Safety
Some examples of products developed through Arago
[one_half][box]

Night-vision driving glasses
These glasses are designed for driving at night, and prevent the driver being dazzled by car lights. They were designed in close collaboration with Valéo.
These glasses use two combined effects: absorption and reflection. This is possible due to a blend of liquid crystals and absorbent material, which creates a variable density. This technology is the result of several years’ research. Several patents have been registered, and have been licensed to the industrial partner.
[/box][/one_half]
[one_half_last][box]

Holographic marking to fight counterfeiting
This marking was entirely designed by Arago. Micro-optics are integrated in banknotes, for example, to fight counterfeiting. The come in the form of holographic films or strips. Their manufacture uses a copying system which reduces production costs, making mass production possible. The work was carried out in close collaboration with industrial partner Surys. Patents have been registered and transferred. The project also led to a copying machine being created for the industrial partner. The machine is currently being used by the company.
[/box][/one_half_last]
[box type=”shadow” align=”” class=”” width=””]
![]() The TSN Carnot institute, a guarantee of excellence in partnership-based research since 2006
The TSN Carnot institute, a guarantee of excellence in partnership-based research since 2006
Having first received the Carnot label in 2006, the Télécom & Société numérique Carnot institute is the first national “Information and Communication Science and Technology” Carnot institute. Home to over 2,000 researchers, it is focused on the technical, economic and social implications of the digital transition. In 2016, the Carnot label was renewed for the second consecutive time, demonstrating the quality of the innovations produced through the collaborations between researchers and companies. The institute encompasses Télécom ParisTech, IMT Atlantique, Télécom SudParis, Télécom, École de Management, Eurecom, Télécom Physique Strasbourg and Télécom Saint-Étienne, École Polytechnique (Lix and CMAP laboratories), Strate École de Design and Femto Engineering.[/box]





Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!